izacoil consulting group
We strive to provide high-quality service and support with our diverse range of activities

the art of commodity trading

expanding tank storage
Expanding tank storage facilities and agreements in Rotterdam, Fujairah and Mersin reflects our commitment to strengthening global logistics capabilities and enhancing regional energy infrastructure. These strategic expansions aim to increase storage capacity.
oil and gas
Implementation of Oil & Gas Enterprise Solutions involves deploying integrated systems that streamline operations, enhance data visibility, and improve decision-making across exploration, production, refining, and distribution activities.
shipping
Registering a new shipping line in Europe requires not only navigating the intricate web of maritime regulations but also aligning with both national and EU-level frameworks that govern commercial maritime operations.

venture agreements
Expanding joint venture agreements with the most famous refineries represents a strategic move toward greater market influence, resource security, and technological collaboration.
ceo message
izac consulting group has a reputation of conducting business with honesty and intergrity. We are proud of our achievements and believe our continued success is possible because of the people we work with.
Looking ahead, we are focused on accelerating the execution of our growth strategy while continuing to build on the strength of our brand-in helping our clients share knowledge and create innovation and in bringing positive change to the commodity trades and risk management communities in which we work and live. I am incredibly excited about this journey and truly believ the best of Trading Company is yet to come.
ali toushkan
CEO & Founder
our services
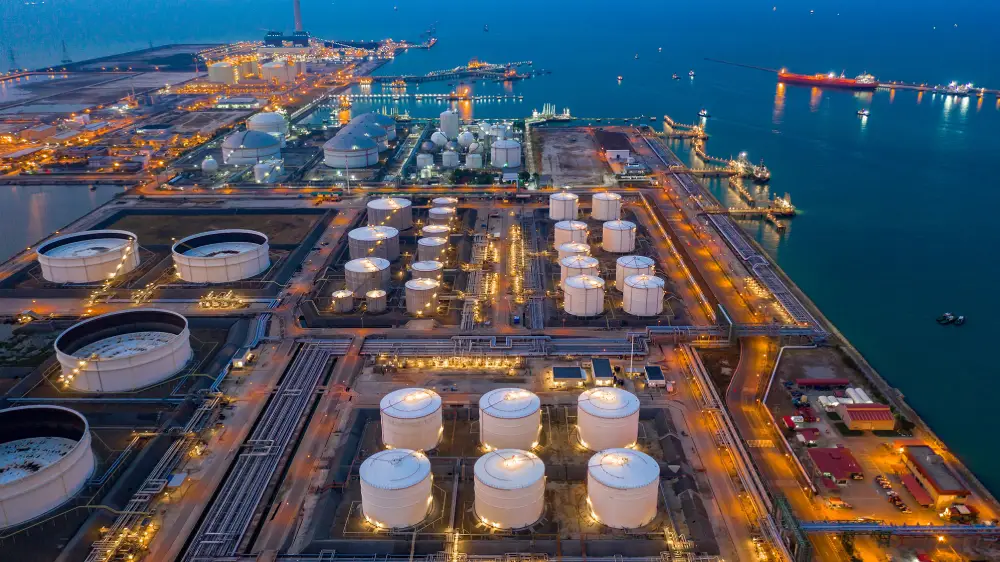

Tank Storage and Facilities
Tank storage services are essential for the global oil and gas industry, as they provide safe and efficient storage and transportation of various petroleum products. Rotterdam and Fujairah are two of the most important locations for tank storage services, as they are strategically located at major shipping routes and supply hubs. our company can facilitate renting of Barge Storage, Vessel Storage, Tank Storage in ROTTERDAM, HOUSTON, and FUJAIRAH PORT, For further information and contract details please contact us.
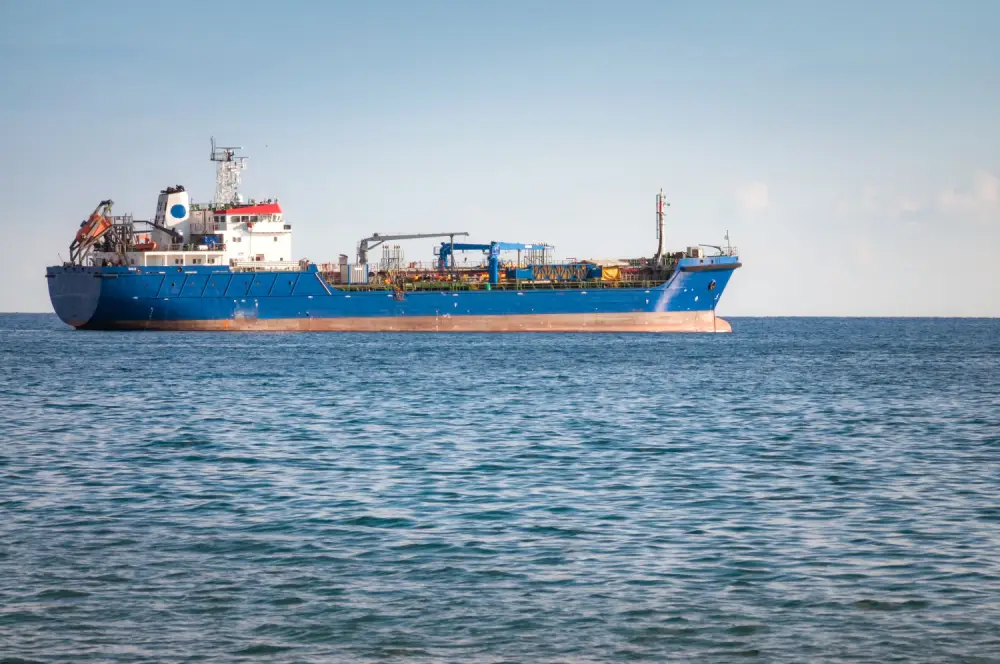

Marin Shipping Services
Marine Shipping offers its services within ordinary dry cargo and oil and gas chartering, ships operation and terminal handling. With our global network, we can always find a suitable solution for your transport. Chartering from coaster vessels up to VLCC for any bulk and break bulk materials worldwide Cargo handling and storage services in ports of loading and discharge Client oriented Charter Party negotiations and supervision Operational and post fixture assistance to our Clients Freight indications for any inquiries.

Commodity Trade And Risk Management
We have a dynamic small team focusing on the Sale and Purchase of the petroleum products. Our resources and expertise help our clients successfully buy and sell oil and gas commodities. We’re experienced in contract management process and guarantee the safe payment transactions.
our products

crude oil
Crude oil, also known as petroleum or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of hydrocarbons, chiefly carbon and hydrogen, that is found in geological formations beneath the Earth’s surface. It is a vital resource that has played a central role in global energy production and economic development for over a century.
Formation and Composition
Crude oil is a fossil fuel, believed to have originated from the decomposition of organic matter, such as algae and plankton, over millions of years under immense heat and pressure. This organic matter gradually transformed into a complex mixture of hydrocarbons, ranging from light and volatile compounds to heavier and more viscous ones. The exact composition of crude oil varies depending on its geological source, but it typically consists of 82-87% carbon and 12-15% hydrogen, with trace amounts of other elements like sulfur, nitrogen, and oxygen.
Extraction and Processing
Crude oil is extracted from underground reservoirs through drilling wells. The extracted oil, known as “raw crude,” undergoes a process called refining to separate it into various petroleum products, such as gasoline, diesel fuel, jet fuel, lubricants, and asphalt. Refining involves a series of distillation, cracking, and chemical treatment steps that break down the complex hydrocarbon molecules into more manageable and usable forms.
Global Significance
Crude oil is the world’s primary source of transportation fuel, accounting for over half of the global energy demand. It is also a crucial feedstock for the production of petrochemicals, which are essential components in a wide range of products, from plastics and synthetic fibers to pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.
Environmental Impact
The extraction, transportation, and refining of crude oil have significant environmental impacts. Oil spills and leaks can contaminate marine and terrestrial ecosystems, harming wildlife and disrupting natural processes. The combustion of petroleum products releases greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide, contributing to climate change.
Transition to Sustainable Energy
As concerns about climate change and environmental degradation grow, there is a growing push to transition away from fossil fuels like crude oil and towards renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and geothermal power. However, crude oil is expected to remain an important part of the global energy mix for many years to come as the world grapples with the challenges of transitioning to a sustainable energy future.

diesel fuel en590
EN 590 specifies the physical and chemical properties that all automotive diesel fuel must meet in order to be sold in the European Union. These properties include:
- Sulphur content: The sulphur content of EN 590 diesel must be no more than 10 parts per million (ppm). This is a significant reduction from the previous standard of 500 ppm.
- Cetane number: The cetane number of EN 590 diesel must be no less than 51. This is a measure of the ignition quality of the fuel.
- Flash point: The flash point of EN 590 diesel must be no less than 32 degrees Celsius. This is the temperature at which the fuel will give off enough vapour to ignite.
- Density: The density of EN 590 diesel must be between 820 and 845 kilograms per cubic metre.
- Kinematic viscosity: The kinematic viscosity of EN 590 diesel must be between 2.0 and 4.5 mm2/s at 40 degrees Celsius. This is a measure of the flow resistance of the fuel.
- Fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) content: The FAME content of EN 590 diesel must be no more than 7% by volume. FAME is a biodiesel component.
EN 590 diesel is also known as ultra-low sulphur diesel (ULSD). This is because the sulphur content of ULSD is much lower than that of traditional diesel fuel. This has a number of environmental benefits, including:
- Reduced emissions of sulphur dioxide (SO2): SO2 is a major contributor to acid rain.
- Reduced emissions of particulate matter (PM): PM can cause respiratory problems.
- Reduced emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx): NOx can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone, which is a harmful pollutant.
In addition to the environmental benefits, ULSD also has a number of performance benefits. These include:
- Improved engine performance: ULSD can help to improve engine efficiency and reduce emissions.
- Reduced wear and tear on engine components: ULSD can help to reduce wear and tear on engine components, such as injectors and pumps.
- Extended engine life: ULSD can help to extend the life of an engine.
EN 590 is the standard for automotive diesel fuel in the European Union. It is a high-quality fuel that has a number of environmental and performance benefits.

lpg
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), also known as propane or LP gas, is a flammable mixture of hydrocarbon gases, primarily propane, propylene, and butane. It is a versatile and efficient fuel that is widely used in various applications, including heating, cooking, transportation, and industrial processes.
Properties of LPG
- Flammable: LPG is a highly flammable gas, and its vapors can easily ignite. Proper handling and storage are crucial to prevent fire hazards.
- Colorless and Odorless: In its natural state, LPG is colorless and odorless. However, an odorant, usually ethanethiol, is added to give it a distinct smell that helps detect leaks.
- Liquefaction: LPG is easily liquefied under moderate pressure. This property makes it convenient for storage and transportation.
- Low Boiling Point: LPG has a low boiling point, allowing it to vaporize easily at standard atmospheric pressure. This property makes it suitable for use in various appliances.
Uses of LPG
- Heating: LPG is a clean and efficient fuel for heating homes, offices, and industrial buildings. It is also commonly used for portable heaters and outdoor cooking appliances.
- Cooking: LPG is a popular fuel for cooking due to its cleanliness, ease of control, and consistent heat output. It is widely used in households, restaurants, and commercial kitchens.
- Transportation: LPG is increasingly used as an alternative fuel for vehicles due to its lower emissions and cleaner combustion compared to gasoline and diesel. It is particularly popular for taxis, buses, and fleet vehicles.
- Industrial Applications: LPG serves as a versatile fuel in various industrial processes, including metal cutting, food processing, and asphalt production. It is also used as a refrigerant and aerosol propellant.
Advantages of LPG
- Clean Burning: LPG produces fewer emissions compared to gasoline and diesel, reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas contributions.
- Energy Efficiency: LPG is an energy-dense fuel, providing more heat and energy per unit volume compared to other fuels.
- Versatility: LPG can be used in a wide range of applications, making it a versatile fuel for various needs.
- Storage and Transportation: LPG is easily stored and transported in pressurized containers, making it convenient for distribution and use.
Safety Considerations
- Handling and Storage: LPG should be handled with care and stored in well-ventilated areas away from heat sources and ignition points.
- Leak Detection: LPG appliances and storage tanks should be regularly inspected for leaks, and an odorant should be properly added to detect them.
- Emergency Procedures: Familiarize yourself with emergency procedures in case of a gas leak or fire.

jet fuel a1
Jet Fuel A1 is a type of aviation fuel designed to be used in turbine-engines aircraft. It is a colorless to straw-colored liquid with a flash point above 38 °C (100 °F) and a maximum freezing point of -47 °C (-53 °F). It is produced to a standardized international specification, known as DEF STAN 91-91 (Jet A-1).
Jet Fuel A1 is the most widely used type of aviation fuel in the world. It is used in both commercial and military aircraft. It is a highly refined fuel that is free of impurities and contaminants. This ensures that it will burn cleanly and efficiently in turbine engines.
Jet Fuel A1 is produced from crude oil. It is fractionally distilled from crude oil to produce a kerosene-type fuel. The kerosene is then further refined to meet the strict specifications of Jet Fuel A1.
Jet Fuel A1 is stored and transported in tanks and pipelines that are lined with a special type of coating. This coating is designed to prevent corrosion and contamination of the fuel.
Jet Fuel A1 is a hazardous material and must be handled with care. It is important to wear personal protective equipment, such as gloves and goggles, when handling Jet Fuel A1.
Here are some of the properties of Jet Fuel A1:
- Flash point: Above 38 °C (100 °F)
- Freezing point: Maximum of -47 °C (-53 °F)
- Boiling point: 176 °C (349 °F; 449 K)
- Density: 775-840 g/L
- NFPA 704 (fire diamond): 2 2 0
Jet Fuel A1 is a vital part of the aviation industry. It is a safe and efficient fuel that allows aircraft to fly long distances and carry heavy payloads.

fuel oil
Fuel oil, also known as furnace oil or heavy fuel oil (HFO), is a category of fuel oils that are obtained from the distillation of crude oil. It is a heavy, viscous liquid that is used in a variety of applications, including power generation, heating, and marine transportation.
Sure, here is a summary of fuel oil:
Fuel Oil
Fuel oil, also known as furnace oil or heavy fuel oil (HFO), is a category of fuel oils that are obtained from the distillation of crude oil. It is a heavy, viscous liquid that is used in a variety of applications, including power generation, heating, and marine transportation.
Types of Fuel Oil
There are six main types of fuel oil:
- No. 1 fuel oil: This is the lightest and cleanest type of fuel oil. It is used in residential and commercial boilers.
- No. 2 fuel oil: This is a slightly heavier and less clean type of fuel oil than No. 1 fuel oil. It is also used in residential and commercial boilers.
- No. 4 fuel oil: This is a heavier and more viscous type of fuel oil than No. 1 or No. 2 fuel oil. It is used in industrial boilers and furnaces.
- No. 5 fuel oil: This is a very heavy and viscous type of fuel oil. It is used in industrial boilers and furnaces, and it is also sometimes used as a bunker fuel for ships.
- No. 6 fuel oil: This is the heaviest and most viscous type of fuel oil. It is used almost exclusively as a bunker fuel for ships.
- Residual fuel oil: This is a type of fuel oil that is produced as a byproduct of the refining process. It is heavier and more viscous than No. 6 fuel oil, and it is often used as a blending stock for other types of fuel oil.
Uses of Fuel Oil
Fuel oil is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Power generation: Fuel oil is used to generate electricity in power plants.
- Heating: Fuel oil is used to heat homes, businesses, and industrial buildings.
- Marine transportation: Fuel oil is the primary fuel source for ships.
- Industrial applications: Fuel oil is used in a variety of industrial applications, such as asphalt production and steelmaking.
Advantages of Fuel Oil
Fuel oil has several advantages over other types of fuel, including:
- High energy density: Fuel oil has a high energy density, which means that it can store a lot of energy in a small volume.
- Low cost: Fuel oil is a relatively low-cost fuel compared to other types of fuel, such as natural gas and propane.
- Readily available: Fuel oil is readily available in most parts of the world.
Disadvantages of Fuel Oil
Fuel oil also has several disadvantages, including:
- High sulfur content: Fuel oil has a high sulfur content, which can contribute to air pollution.
- Low efficiency: Fuel oil is a relatively inefficient fuel, which means that it releases a lot of heat for the amount of energy it produces.
- Environmental impact: The combustion of fuel oil can release a variety of pollutants into the atmosphere, including sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter.
Future of Fuel Oil
The use of fuel oil is likely to decline in the future as a result of environmental concerns and the development of cleaner alternatives. However, fuel oil is likely to remain an important fuel source for some applications, such as marine transportation, for the foreseeable future.
diesel gas d2 oil
Diesel Gas Oil (D2) is a middle distillate fuel that is produced from crude oil. It is a clear, light yellow liquid that is used in a variety of applications, including transportation, power generation, and heating. D2 is a relatively clean fuel, with low sulfur content and emissions. It is also a very efficient fuel, with a high energy density.
Production
D2 is produced from crude oil through a process called fractional distillation. Crude oil is heated to a high temperature, which causes it to vaporize. The vapors are then condensed into different fractions, based on their boiling points. D2 is one of the middle distillates, which means that it has a higher boiling point than gasoline but a lower boiling point than heavier fuel oils.
Uses
D2 is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Transportation: D2 is the primary fuel for diesel engines, which are used in a wide variety of vehicles, including trucks, buses, cars, and trains.
- Power generation: D2 can be used to generate electricity in diesel generators.
- Heating: D2 can be used to heat homes and businesses.
- Industrial uses: D2 is used in a variety of industrial applications, such as asphalt production and manufacturing.
Advantages
D2 has a number of advantages over other fuels, including:
- Low sulfur content: D2 has a very low sulfur content, which means that it produces fewer emissions than other fuels.
- High energy density: D2 has a high energy density, which means that it can provide more power per gallon than other fuels.
- Efficient combustion: D2 burns very efficiently, which means that it produces less waste and pollution than other fuels.
- Relatively clean fuel: D2 is a relatively clean fuel, with low levels of emissions and pollutants.
Disadvantages
D2 also has a few disadvantages, including:
- High cost: D2 is a relatively expensive fuel.
- Limited availability: D2 is not as widely available as some other fuels.
- Storage requirements: D2 must be stored in a cool, dry place to prevent it from degrading.
Overall, D2 is a versatile and efficient fuel that is used in a variety of applications. It is a relatively clean fuel with low sulfur content and emissions. However, it is also a relatively expensive fuel and not as widely available as some other fuels.

virgin fuel oil d6
Virgin Fuel Oil D6: A Heavy Fuel with Many Uses
Virgin Fuel Oil D6, also known as residual fuel oil (RFO) or Bunker C, is a heavy fuel oil used in large ships, power plants, and industrial boilers. It is a low-grade fuel oil that is produced from the residue remaining after crude oil has been refined into lighter products, such as gasoline and diesel. Because it is a low-grade fuel, D6 is less expensive than other types of fuel oil, but it is also more polluting.
Specifications
- Viscosity: D6 is a high-viscosity fuel oil, which means that it is thick and slow-flowing. This makes it necessary to preheat D6 before it can be used.
- Sulfur content: D6 has a high sulfur content, which can cause air pollution. In recent years, there have been stricter regulations on the sulfur content of D6, which has led to the development of low-sulfur D6 (LSD6).
- Ash content: D6 has a high ash content, which can cause problems in boilers and engines.
Uses
D6 is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Marine fuel: D6 is the most common type of fuel oil used in large ships.
- Power generation: D6 is used to generate electricity in power plants.
- Industrial boilers: D6 is used to provide heat in industrial settings.
Advantages
- Low cost: D6 is a low-grade fuel oil, which makes it less expensive than other types of fuel oil.
- High energy density: D6 has a high energy density, which means that it can store a lot of energy in a small volume.
Disadvantages
- High sulfur content: D6 has a high sulfur content, which can cause air pollution.
- High ash content: D6 has a high ash content, which can cause problems in boilers and engines.
- Requires preheating: D6 is a high-viscosity fuel oil, which means that it must be preheated before it can be used. This can be costly and time-consuming.
Overall, Virgin Fuel Oil D6 is a low-cost, high-energy fuel oil that is used in a variety of applications. However, it is important to note that D6 is a polluting fuel oil, and there are stricter regulations on its sulfur content in recent years.

lng
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) is natural gas that has been cooled to a liquid state (around -260°F) for ease and safety of storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volume of natural gas in its gaseous state at standard atmospheric pressure and temperature. LNG is odorless, colorless, non-toxic and non-corrosive.
LNG is produced by cooling natural gas to a very low temperature. This process is called liquefaction. Liquefaction reduces the volume of natural gas by about 600 times, making it much easier to store and transport. LNG can be stored in specially designed tanks and transported by ship.
LNG is a clean-burning fuel that produces lower emissions of greenhouse gases than other fossil fuels. It is also a relatively safe fuel to transport and store. LNG is becoming an increasingly important source of energy around the world.
Uses of LNG
LNG is used for a variety of purposes, including:
- Power generation: LNG can be used to generate electricity in power plants.
- Heating: LNG can be used to heat homes and businesses.
- Transportation: LNG can be used to power ships, trucks, and buses.
- Industrial uses: LNG can be used as a feedstock for the production of chemicals and fertilizers.
Advantages of LNG
LNG has several advantages over other fossil fuels, including:
- Lower emissions: LNG produces lower emissions of greenhouse gases than other fossil fuels, such as coal and oil.
- Clean burning: LNG is a relatively clean-burning fuel. It produces less soot and other pollutants than other fossil fuels.
- Safe to transport and store: LNG is a relatively safe fuel to transport and store. It is not as flammable as other fossil fuels, such as gasoline.
Disadvantages of LNG
LNG also has some disadvantages, including:
- Cost: LNG is a more expensive fuel than other fossil fuels.
- Infrastructure: LNG requires a specialized infrastructure for transportation and storage.
- Safety: LNG can be dangerous if not handled properly. It can cause frostbite and asphyxiation.
Future of LNG
LNG is an important part of the global energy mix. It is a clean-burning fuel that can help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. LNG is also a versatile fuel that can be used for a variety of purposes. The demand for LNG is expected to grow in the coming years as countries seek ways to reduce their reliance on traditional fossil fuels.
Overall, LNG is a valuable energy resource that has the potential to play an important role in the global energy mix.

fuel oil cst-180
Fuel Oil CST-180 is a heavy fuel oil (HFO) with a kinematic viscosity of 180 centistokes (cst) at 50°C. It is a residual fuel oil, which means it is the remaining product after the distillation of crude oil. HFO is typically used in marine boilers and industrial furnaces.
CST-180 is a relatively low-sulfur HFO, with a sulfur content of 2.0% or less. This makes it compliant with the International Maritime Organization (IMO) 2020 sulfur cap regulations. The IMO 2020 sulfur cap limits the sulfur content of HFO used in marine vessels to 0.5%.
CST-180 is a versatile fuel oil that can be used in a variety of applications. Some of the most common uses of CST-180 include:
- Marine boilers: CST-180 is the most common type of HFO used in marine boilers. It is a dense, high-energy fuel that is well-suited for burning in marine boilers.
- Industrial furnaces: CST-180 is also used in industrial furnaces, where it is used to generate heat for a variety of processes.
- Cement kilns: CST-180 is sometimes used as a fuel in cement kilns.
- Power plants: CST-180 can also be used in power plants, where it is used to generate electricity.
CST-180 is a relatively low-cost fuel oil. This makes it an attractive option for a variety of applications. However, CST-180 is also a relatively dirty fuel oil, which means it can produce emissions that are harmful to the environment.
Overall, CST-180 is a versatile and economical fuel oil that can be used in a variety of applications. However, it is important to be aware of the environmental impacts of CST-180 before using it.
Here are some of the properties of CST-180:
- Kinematic viscosity: 180 cSt at 50°C
- Density: 0.95 kg/L at 15°C
- Sulfur content: 2.0% or less
- Flash point: 60°C (140°F)
- Ash content: 0.1% or less
- Water content: 1.0% or less

ago
Automotive Gas Oil (AGO), also known as diesel fuel, is a type of liquid fuel that is used in compression-ignition engines. It is a petroleum product that is produced by fractional distillation of crude oil. AGO is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons, and its composition varies depending on the source of the crude oil and the refining process.
AGO is a relatively clean-burning fuel, with low emissions of sulfur and nitrogen oxides. It is also more efficient than gasoline, meaning that it produces more energy per unit of volume. As a result, AGO is the fuel of choice for most heavy-duty vehicles, such as trucks, buses, and tractors.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in using AGO in passenger cars. This is due in part to the development of new, cleaner diesel engines. AGO-powered cars can offer better fuel economy and lower emissions than gasoline-powered cars.
However, there are some drawbacks to using AGO. AGO is more expensive than gasoline, and it can be more difficult to find AGO fueling stations. Additionally, AGO can produce higher levels of particulate matter emissions than gasoline.
Despite these drawbacks, AGO is a promising alternative fuel for passenger cars. As diesel engine technology continues to improve, AGO is likely to become a more popular choice for drivers.
Here are some of the key properties of Automotive GAS Oil:
- Cetane number: The cetane number is a measure of the ignition quality of AGO. The higher the cetane number, the easier it is for the fuel to ignite.
- Sulfur content: The sulfur content of AGO is a measure of the amount of sulfur in the fuel. The sulfur content of AGO is regulated in many countries to reduce emissions of sulfur oxides.
- Viscosity: The viscosity of AGO is a measure of its resistance to flow. The viscosity of AGO is important because it affects the fuel’s ability to flow through the engine’s fuel system.
- Flash point: The flash point of AGO is the temperature at which the fuel will ignite. The flash point of AGO is important for safety reasons because it indicates how easily the fuel can catch fire.

light cycle oil
Light Cycle Oil (LCO) is a liquid byproduct of the fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) process, a common refining technique used to convert heavy crude oil fractions into lighter, more valuable products like gasoline and diesel. LCO falls within the boiling range of diesel, but it doesn’t meet the quality standards for direct use as diesel fuel due to its poor ignition characteristics, high density, and sulfur content.
Production of Light Cycle Oil
The FCC process involves circulating a mixture of heated oil and catalyst particles into a reaction chamber. As the mixture passes through the catalyst, the catalyst promotes the breaking down of large hydrocarbon molecules into smaller ones, producing lighter products like gasoline and LPG. The heavier hydrocarbons that remain after this initial cracking process are then recycled back into the FCC reactor for further cracking. This recycling process leads to the formation of LCO.
Properties of Light Cycle Oil
LCO is characterized by its:
- High aromatic content: Aromatic hydrocarbons have a ring-shaped structure that contributes to LCO’s low cetane number, a measure of ignition quality in diesel fuels.
- High density: LCO has a higher density than desired diesel fuel, making it less energy-dense.
- High sulfur content: Sulfur emissions from diesel combustion contribute to air pollution, and LCO’s high sulfur content makes it unsuitable for direct use as diesel fuel.
Processing of Light Cycle Oil
To transform LCO into a valuable diesel fuel component, it undergoes further processing steps:
- Hydrotreating: This process removes sulfur and nitrogen compounds from LCO, improving its environmental profile and cetane number.
- Isomerization: This process rearranges the molecular structure of some of the aromatic hydrocarbons in LCO, further improving its cetane number.
After these processing steps, the resulting product, known as hydrotreated light cycle oil (HLCO), meets the quality standards for blending into diesel fuel.
Applications of Light Cycle Oil
Apart from its use as a diesel fuel component, LCO has other applications:
- Feedstock for further processing: LCO can be used as a feedstock for producing other valuable products, such as lubricants, solvents, and waxes.
- Asphalt blending: LCO can be blended with asphalt to improve its properties and performance.
Future of Light Cycle Oil
As the demand for clean diesel fuel grows, LCO is expected to play an increasingly important role in the refining industry. Advances in processing technologies and catalyst development will likely lead to more efficient and cost-effective ways to transform LCO into high-quality diesel fuel components.

urea 46% prilled & granular
UREA 46% PRILLED & GRANULAR
Urea 46% prilled and granular is a high-nitrogen fertilizer that is commonly used in agriculture. It is a white, crystalline solid that is soluble in water. Urea is produced by the reaction of ammonia and carbon dioxide. It is the most concentrated nitrogen fertilizer available, containing 46% nitrogen by weight.
Benefits of UREA 46% PRILLED & GRANULAR
- High nitrogen content (46%)
- Soluble in water
- Easy to apply
- Relatively inexpensive
Uses of UREA 46% PRILLED & GRANULAR
- Lawn fertilizer
- Garden fertilizer
- Topdressing for cereal crops
- Foliar fertilizer
- Animal feed supplement
Application rates for UREA 46% PRILLED & GRANULAR
The application rate of urea will vary depending on the crop, soil type, and desired nitrogen level. However, a general rule of thumb is to apply 1 pound of urea per 1,000 square feet of lawn or garden.
Safety precautions for UREA 46% PRILLED & GRANULAR
- Urea is a mild irritant to the skin and eyes. Wear gloves and goggles when handling urea.
- Urea can be harmful if swallowed. Keep urea out of reach of children.
- Do not apply urea to frozen ground or when rain is expected.
Storage of UREA 46% PRILLED & GRANULAR
- Store urea in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
- Urea can absorb moisture, so it is important to keep it sealed in an airtight container.
Overall, UREA 46% PRILLED & GRANULAR is a versatile and effective fertilizer that can be used in a variety of applications. However, it is important to use it safely and follow the recommended application rates.